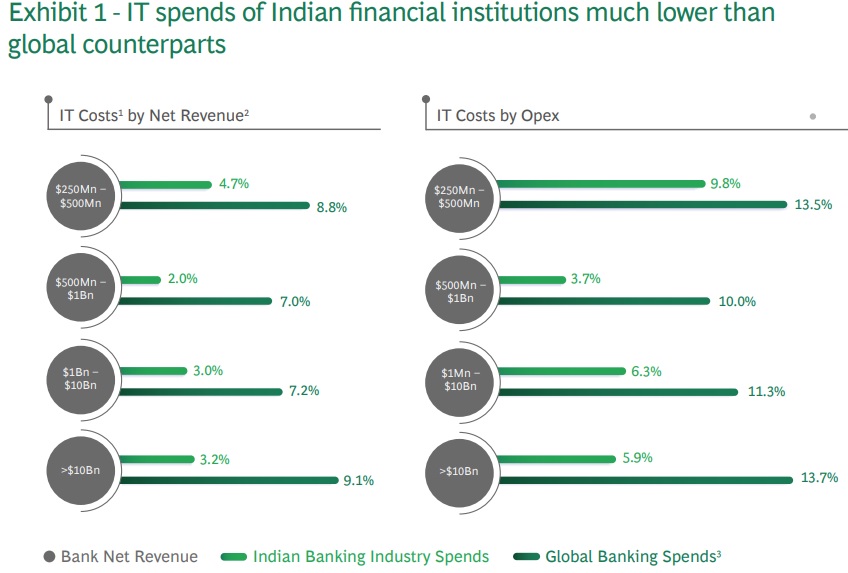
BCG India Report identifies low IT investment, legacy core systems, and regulatory compliance as major challenges
FinTech BizNews Service
Mumbai, August 1, 2024: India’s BFSI sector has seen rapid digitalization, however, innovations in fintech, driven by Artificial Intelligence, cloud computing, and digitalization, have far outpaced traditional banking, which continues to rely on legacy core systems. According to the BCG, nearly 75% of digital payments and loans, and 25% of new digital accounts are likely to originate from third-party platforms by FY26.
BCG India’s latest report "Navigating the Journey to Cloud-based Core Transformations," provides a comprehensive analysis of the challenges and opportunities facing Indian financial institutions and the transformation potential and strategies for transitioning to cloud-based core systems. The report highlights critical insights and strategies that can enable banks to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations.
The report identifies key challenges that Indian banks face, including
Keeping up with emerging digital trends, skyrocketing customer expectations, and meeting regulatory requirements makes it imperative for financial institutes to modernize their core systems by transitioning to cloud-based solutions. As customer expectations continue to evolve, fuelled by digital innovations in other sectors, banks must adopt new technologies to offer seamless, personalized services. The rise of fully online, digitally native lenders and neobanks is setting new standards for speed and customer service, pressuring traditional banks to keep pace.
The report also further identifies how banks can invest in emerging technology architectures, new-age talent and service providers, as well as implementation of agile methodologies in fostering cross-functional collaboration to ensure effective core transformation.
Offering customizable solutions for varying organizational needs, the report identifies five innovative solutions across two primary archetypes for core modernization. The selection of an appropriate strategy depends on several factors, including the institution's readiness for business transformation, the complexity of the core system, execution speed, internal IT maturity, cost appetite, and risk tolerance.
Key Strategies for Core Mordernization
As the Indian financial sector continues to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, this report provides crucial insights into the path forward. By embracing cloud-based core transformations, Indian banks can not only overcome current challenges but also position themselves for future growth and success.