China Ban On Critical Minerals: Impact On India; Transport Equipment, Basic Metals, Machinery, Construction and Electrical & Electronics. Both domestic production and exports will be impacted;
FinTech BizNews Service
Mumbai, July 28, 2025: The State Bank of India’s Economic Research Department has come out with a Research Report titled “China’s ban on Rare Earth and Permanent Magnets: Implications for India”, authored by Dr. Soumya Kanti Ghosh, Group Chief Economic Advisor, State Bank of India.
Critical minerals are important for modern economic structures
❑ Critical minerals form an important part of the modern economic production process
❑ Criticality of a mineral is decided by many factors notably –
• Current and emerging economic structure
• Technology
• Local availability and
• Technologically feasible substitute
❑ Therefore, what is critical is depends on country under study
❑ Economically critical minerals are characterized by following properties
• Small share in overall cost structure but extreme criticality in production
• Concentrated supply sources resulting in sudden reduction in capacity utilization due to disruption
• Nonavailability of substitutes and recycling technology
• Opaque pricing, high price volatility and geopolitical risk
National policy on critical minerals and banks
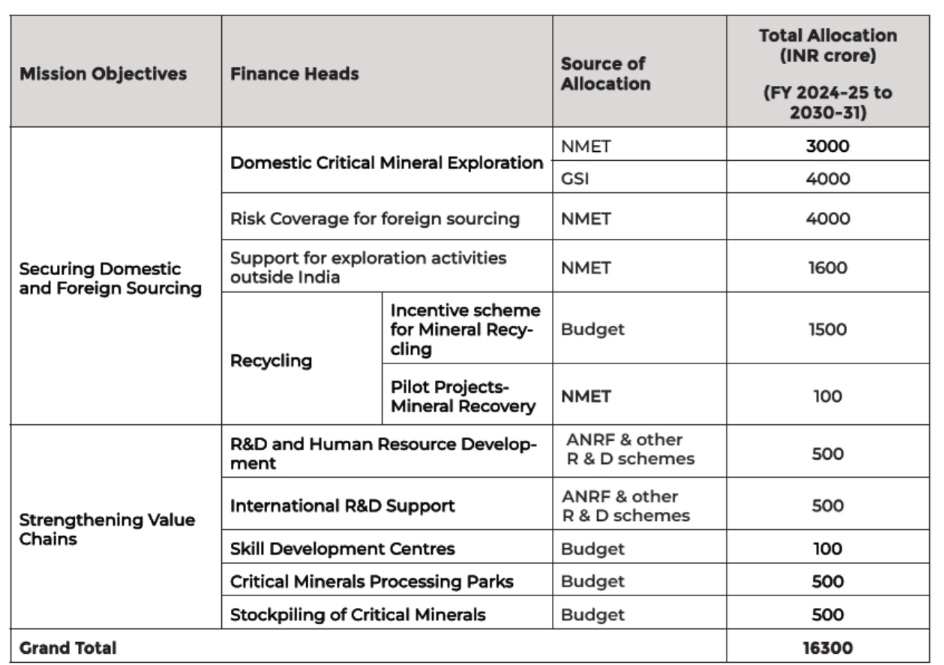
❑ Finance Minister announced setting up of ‘Critical Mineral
Mission’ in the Union Budget speech 2024-25 on
23.07.2024
❑ Government of India has launched the National Critical
Mineral Mission (NCMM) in 2025 to establish a robust
framework for self-reliance in the critical mineral sector
❑ India will invest in exploring and acquiring critical mineral
assets in resource-rich countries
❑ PSUs and private firms will be supported through funding,
guidelines, and inter-ministerial coordination
❑ Accordingly, critical minerals are an important business
opportunity for banks that requires exclusive policy focus
and strategic direction within banks
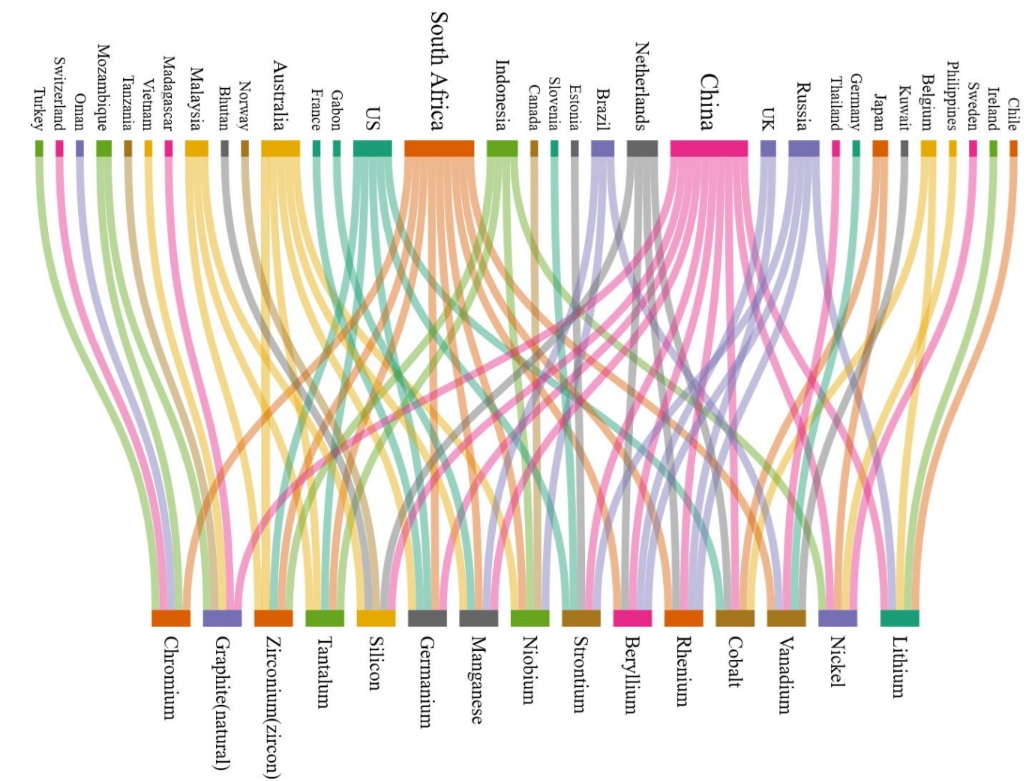
30 critical minerals have been identified Ministry of Mines, Government of India
Critical minerals include a wide range of minerals and compounds. This analysis is based on rare earth which is a subset of larger critical mineral set and includes minerals banned by China
Funds allocation has neem made under Critical Mineral Mission. Network topology is reflected in the chart for 15 Critical mineral for India with near 100% import dependency. (Source: Report of the Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals, Ministry of Mines June 2023)
Economic importance of rare earth increasing due to digitization and green transition
❑ Rare earth is a subset of critical mineral with wide
application in many emerging technologies
❑ During the last three decades, there has been an
explosion in the applications of rare earth and their
alloys in several technology devices
❑ Because of their unique physical, chemical, magnetic,
luminescent properties, these elements help to make
many technological advantages such as reduced energy
consumption, miniaturization, durability and thermal
stability
❑ In recent years, demand for rare earth is particularly on
rise in energy efficient gadgets (green technology) which
are faster, lighter, smaller and more efficient
Areas of Application
Electronics:
Television screens, computers, cell phones,
silicon chips, long-life rechargeable batteries,
camera lenses, LED, CFL, marine propulsion
systems
Manufacturing:
High strength magnets, stress gauges, ceramic
pigments, colorants in glassware, chemical
oxidizing agent, automotive catalytic converters
Medical Science:
Portable X-ray machines, MRI, contrast agents,
nuclear medicine imaging, cancer treatment
applications, and for genetic screening tests,
medical and dental lasers
Renewable Energy:
Hybrid automobiles, wind turbines, next
generation rechargeable batteries, biofuel
catalysts
Technology:
Lasers, optical glass, fiber optics, masers, radar
detection devices, nuclear fuel rods, mercury-
vapor lamps, highly reflective glass, computer
memory, nuclear batteries, high temperature
superconductors
Import of rare earth permanent magnets by India has increased sharply
India’s consumption of rare earth minerals and compounds shows rising trend in volumes. China dominates in India’s direction of trade in rare earth minerals and compounds. Import of rare earth permanent magnets by India has increased sharply in FY25. Trends in prices of select rare earth minerals (USD / kg) shows high volatility. Granular analysis shows, absorption of rare earth and magnets concentrated in four sectors.
Economic importance of rare earth significant for transport, basic metals and electronics
❑ The analysis indicates that total imports of rare earth and compounds is around $33 million per year in the last
four years. FY25 imports at $31.9 million
❑ The imports of magnets averaged $249 million in last four years. In FY25 magnet imports were $291 million
❑ The analysis indicates direct absorption of rare earth is concentrated in six sectors, with sizable absorption in
basic metals and electrical and optical equipment
Rare earth footprint: a banking perspective under aggravated scenario....
❑ Rare earth being a critical mineral, disruption in supply of rare earth can impact the financial exposure
of banks to these sectors as also ancillary ones
❑ However, it should be kept in mind vulnerability is also a function of available inventory of rare earth
and disruption is not immediate uniformly across sectors
❑ The possible transmission mechanism to banks due to rare earth supply shock under aggravated
scenario may include
• Elongation of working capital cycle due to accumulation of semi-processed inventory, idle capacity
etc.
• Volatility in demand due to output inoperability
• Likely emergence of stress in both upstream and downstream sectors
• Interlinkages from NBFC sector to banking sector
• Export / trade uncertainties for committed yet unfulfilled obligations; both funds as also non-funds
based (due to sudden restrictions)
❑ The latest RBI FSR acknowledges that domestic financial system can be impacted by external
spillovers and intensifying geopolitical hostilities
❑ Since geopolitical factors decide the criticality of a mineral, the above analysis is one of the many
dimensions of impact of geopolitical factors on banking
State government participation in rare earth exploration and value-add manufacturing
❑ Domestic value-chain creation in critical minerals will
require state government participation
❑ Many States have issued Notice Inviting Tenders
(NIT) for the auction of Exploration License (EL)
• Adjoining figures gives NIT & EL as per inviting states
and critical mineral type
❑ The Industrial Policy Resolution 2022 of Odisha
Government recognizes Rare Earth Minerals based
value-added products as a priority sector under the
policy
❑ Odisha Government has approved ₹8000 crore
titanium facility in Ganjam to boost high-tech
manufacturing
❑ Critical mineral value-chains can be source of
regional economic development given the
expanding digital and green economy
❑ The direct absorption of magnets is concentrated in automotive, electrical and electronics and machinery
❑ The granular sector by sector analysis using the direct rare earth input and embodied rare earth in
magnets (@ 33% of weight) was done using two perspective – final demand and export demand
❑ The rare earth footprint (in kg) is an approximate indicator of the vulnerability of the sector output to disruption
in supply of rare earth/rare earth value added
❑ The top sectors impacted by China’s ban include – Transport equipment, basic metals, machinery,
construction and electrical and electronics
❑ Both domestic production and exports will be impacted