Compelling Necessity Of MFIs To Go To Scale
Infomerics Ratings - Outlook report on India’s Microfinance Industry
FinTech BizNews Service
Mumbai, February 16, 2025: Infomerics Ratings has come out with an outlook report on “India’s Microfinance Industry: Compelling Necessity of MFIs to go to scale” by Dr. Manoranjan Sharma, Chief Economist, Infomerics Ratings.
The report provides an insightful view of the performance of Microfinance Industry of India, Loan Outstanding, Bank Credit to MFIs, Risks and Challenges, Delinquency, Institutional Initiatives and Way Forward.
Key highlights of the report are given below:
- The microfinance sector in India has expanded significantly, with 168 Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs) operating across 29 states, serving 64 million borrowers—99% of whom are women. The sector contributes to financial inclusion, rural development, and economic empowerment.
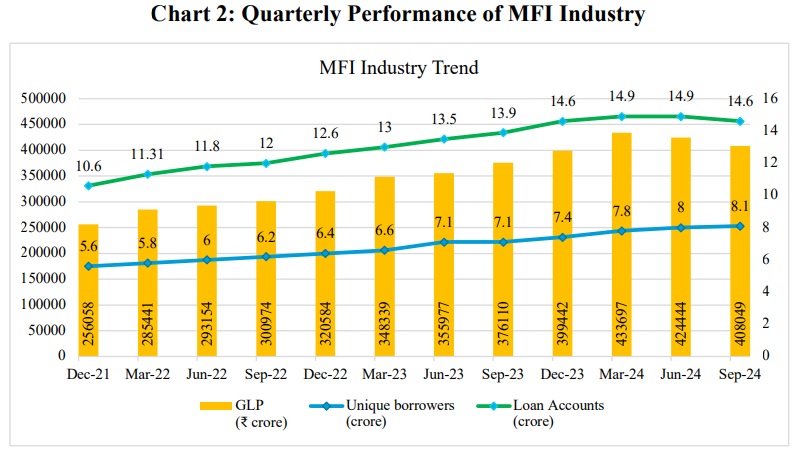
- Over the last decade, Non-Banking Financial Companies-Microfinance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs), regulated by the RBI, have significantly expanded their operations, empowering over 8.1 crore unique borrowers as of September 2024, with an outstanding gross loan portfolio (GLP) of Rs4,08,049 crore and 14.6 crore loan accounts.
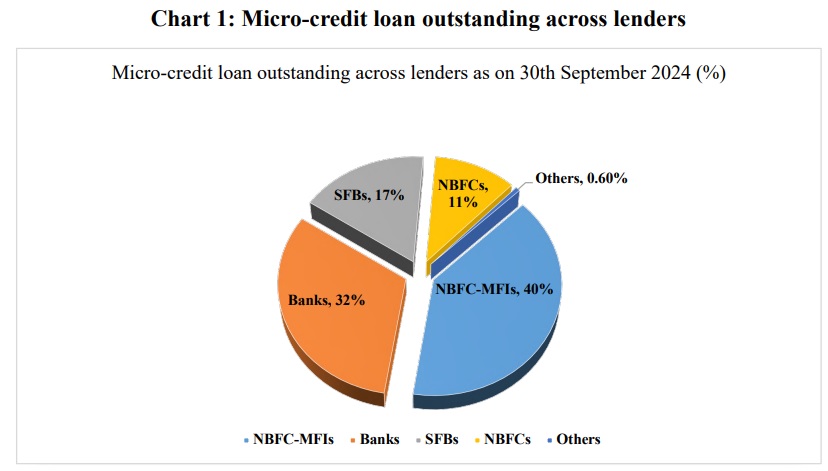
- The industry consists of NBFC-MFIs (39.6%), banks (32.2%), Small Finance Banks (16.9%), and other financial institutions. The gross loan portfolio (GLP) surged from Rs2.56 lakh crore in 2021 to Rs4.08 lakh crore in 2024, contributing 130 lakh jobs and 2% to India’s Gross Value Added (GVA).
- Rising delinquencies (Rs28,154 crore in loans overdue by 31–180 days), borrower over-leveraging (37% of borrowers under stress), high outreach costs, and regulatory scrutiny pose significant risks to the industry.
- As of September 30, 2024, India’s microfinance sector reflects a diverse lending ecosystem, with NBFC-MFIs leading as the largest contributors with a portfolio of Rs1,61,470 crore, accounting for 39.6% of the total industry portfolio.
- The RBI and Microfinance Institutions Network (MFIN) have introduced measures such as capping the number of lenders per borrower at three, implementing stricter lending norms, and increasing government support through enhanced MUDRA limits and the Self-Help Group Bank Linkage Program (SHG-BLP).
- Nearly 98% of loans are provided through the Joint Liability Group (JLG) model, which leverages social collateral to mitigate risk. Repayments are capped at 50% of household income to ensure affordability.
- Future growth in microfinance relies on adopting digital lending platforms, risk mitigation strategies, and funding diversification. Enhanced financial literacy and governance frameworks are also necessary for sustainable expansion.
- Some states, such as Bihar, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and Odisha, account for 62% of total microfinance delinquencies. Rising borrower indebtedness and regulatory tightening in these regions present significant challenges.
- The sector is poised for growth but requires better risk management, alternative funding sources, and stronger policy interventions. Leveraging fintech solutions, improving borrower education, and diversifying loan products will be crucial for its long-term sustainability.